The Past Tense of Grow Explained in Simple Terms
Understanding the Past Tense of Grow
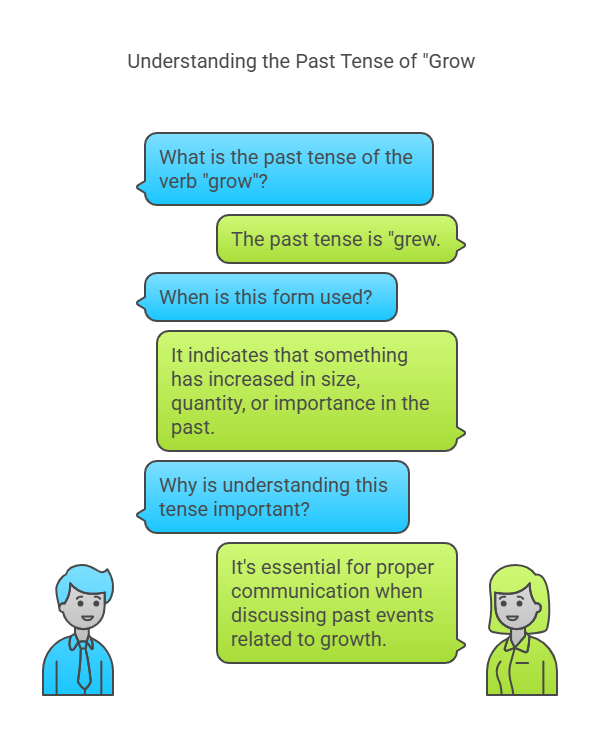
Knowing the past tense of “grow” is fundamental in mastering English grammar. The verb “grow” is one of the most commonly used in the language, yet it often leads to confusion when its past tense form is needed. The common mistake is not distinguishing between its forms or misusing them in different tenses. For example, using “grown” when “grew” is required in the past tense can sound jarring and incorrect to a native speaker. Hence, having a clear understanding of its past tense is critical for both fluent communication and accurate writing.
The Simple Past Tense of Grow: Grew
When to Use Grew in a Sentence
“Grew” is used to describe actions that happened in the past. For example, when you are recounting how something or someone increased in size, improved, or was cultivated over time, the word “grew” should be used. This form is strictly used for simple past-tense actions, without implying anything ongoing or completed over time.
Key Differences Between “Grow” and “Grew”
“Grow” is the present tense form of the verb, while “grew” is its simple past form. The difference is straightforward: “grow” indicates something that is currently happening, whereas “grew” reflects an action that occurred in the past. For example, “The tree grows every year” uses the present tense to indicate an ongoing process, whereas “The tree grew taller last summer” refers to an action that happened at a specific point in the past.
Why Grew is the Correct Past Tense of Grow
The Rule of Regular vs. Irregular Verbs
“Grew” is an example of an irregular verb. In English, verbs are categorized into regular and irregular types. Regular verbs form their past tense by simply adding an “-ed” ending, such as “talk” becoming “talked.” However, irregular verbs, like “grow,” change their form entirely in the past tense. Instead of following a predictable rule, they often shift in unpredictable ways, requiring memorization and practice to get them right.
Examples of the Past Tense of Grow in Sentences
Using “grew” in the correct context is essential for clarity and accuracy.
In personal contexts: “Last year, I grew my own tomatoes for the first time.”
In professional contexts: “The company grew its market share by 10% last quarter.”
In academic contexts: “The research study grew in scope as new data was collected.”
It’s important to remember that “grew” is used for actions that have already been completed. Misusing it by replacing it with “grown” or “grow” can create confusion and weaken the impact of the sentence.
How to Use Grew Correctly in Different Tenses
It’s essential to use “grew” only in the simple past tense. When talking about actions that happened continuously or that were completed, it’s also crucial to pair “grew” with auxiliary verbs in different constructions like the past continuous (“was growing”) or the present perfect (“has grown”).
Mistakes to Avoid When Using Grew
One major mistake to avoid is using “grown” instead of “grew” in a simple past context. “Grown” is used in perfect tenses, not in the simple past. For example, saying “I grown up in a small town” is incorrect. Instead, it should be “I grew up in a small town.”
Common Mistakes with the Past Tense of Grow
Using Grown Incorrectly in Simple Past Contexts
“Grown” is often misused as a simple past tense verb. The past participle form of “grow” is “grown,” but it should be paired with an auxiliary verb, such as “have” or “had,” to create perfect tenses. For instance, “I have grown over the years” is correct in the present perfect tense, but “I grown” would be a grammatical error.
Confusing Grew with Grown in Compound Tenses
When forming compound tenses, such as the present perfect or past perfect, “grown” should be used. For instance, “I have grown a lot since then” uses the correct past participle. Confusing this with “grew” in the same context would make the sentence grammatically incorrect, as in “I have grew,” which is wrong.
How to Master the Past Tense of Grow
Practice Exercises to Reinforce Understanding
To master the past tense, try filling in the blanks with the correct form of “grow.” For example:
- “The flowers ____ taller every day last spring.”
- “I ____ tired after the long hike.”
- “They ____ closer after working together for years.”
Practicing with different sentence structures will help solidify the concept of “grew” as the correct past tense form.
Visual Aids to Connect Grow and Grew with Other Irregular Verbs
Create a chart that connects “grow” with other similar irregular verbs, like “go” (went), “eat” (ate), and “sing” (sang). Seeing how these verbs evolve in their past tense forms will aid in memorization and help you recognize patterns that are common among irregular verbs.
When to Use Grew vs. Grown
Understanding the Difference Between Grew and Grown
While “grew” is the simple past tense form of “grow,” “grown” is its past participle. The past participle form is used when creating perfect tenses or passive constructions. For instance, “I have grown as a person” uses “grown” to indicate personal development over time, while “I grew during my childhood” uses “grew” to refer to a past event.
Examples Comparing Both Forms in Different Sentence Structures
- “I have grown as an artist over the years” (present perfect)
- “I grew as an artist last year” (simple past)
Understanding the distinction between these two forms allows for precise communication, especially when referring to the timing and completion of actions.
Conclusion: Mastering the Past Tense of Grow
The past tense of “grow” is “grew,” and mastering its usage is essential for clear communication. By understanding its irregular form, recognizing common mistakes, and practicing in various contexts, you’ll ensure that you use “grew” correctly and confidently. Remember to avoid confusing “grew” with “grown,” and practice its use in both spoken and written form. With consistent practice, this concept will become second nature.
Source
Harper, Douglas. “Etymology of grow.” Online Etymology Dictionary
My name is Khamis Maiouf. I am the creator of the English Teacher Site, dedicated to providing valuable resources and insights for students around the world. With a passion for education and a commitment to helping students enhance their skills, I aim to make English teaching more effective and enjoyable for both educators and students.