Who vs Whom: The Ultimate Guide You Need to Know

Mastering Who vs Whom Once and For All
The confusion between “who” and “whom” is widespread in both written and spoken English. For many, it seems like a subtle distinction—something that can be ignored in casual conversation. However, understanding the difference is crucial for proper communication, especially in more formal settings.
This guide is designed to demystify the difference between “who” and “whom.” By breaking down the rules and providing clear examples, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to confidently use “who” and “whom” correctly in any situation.
The Basics: Who vs Whom Explained
What Does Who Refer to in a Sentence?
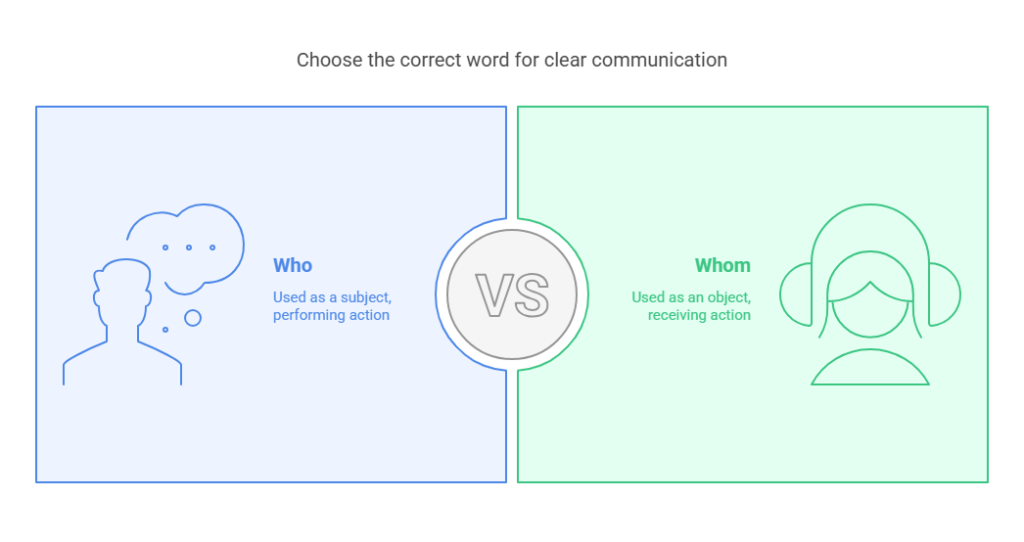
“Who” is a pronoun used as a subject in a sentence. It is employed when referring to the person or people performing the action. In its simplest form, “who” acts as the subject of a verb, answering the question “who is performing the action?”
For example, in the sentence “Who is coming to the party?” “who” is the subject of the verb “is coming.” This structure identifies the person or people responsible for the action.
What Does Whom Refer to in a Sentence?
“Whom,” on the other hand, is a pronoun used as an object in a sentence. It is typically used to refer to the person or people receiving the action of the verb or acting as the object of a preposition. In other words, “whom” is used when the pronoun is the object, not the subject.
For example, in the sentence “To whom did you give the book?” the word “whom” serves as the object of the preposition “to,” indicating the recipient of the action.
The Core Difference Between the Two Words
The core difference between “who” and “whom” lies in their function in a sentence. “Who” is used as a subject, while “whom” functions as an object. This distinction becomes important when writing in more formal English, where the rules of grammar are strictly observed. In casual conversation, people often use “who” in places where “whom” would be grammatically correct, but the use of “whom” is still preferred in formal writing and speech.
When to Use Who
Who as a Subject: The Rule and Examples
“Who” is used when referring to the subject of a verb, that is, the person or group performing the action. It helps identify the doer of the action in the sentence.
For example, “Who is responsible for the project?” Here, “who” is the subject of the verb “is responsible.”
How to Identify When Who is Appropriate
If the word in question is acting as the subject of the sentence, you should use “who.” Ask yourself: “Who is doing the action?” If you can answer this with a person or group, “who” is the correct choice.
For example: “Who invited you to the event?” “Who” is correct because it is asking about the subject—the one doing the inviting.
When to Use Whom
Whom as an Object: The Rule and Examples
“Whom” is used when the pronoun is the object of a verb or preposition. Unlike “who,” which is the subject, “whom” refers to the person or people receiving the action or acting as the object in the sentence.
For example, in “Whom did you meet yesterday?” “whom” is the object of the verb “meet.” It answers the question about the recipient of the action.
How to Identify When Whom is Appropriate
If the word in question is receiving the action (the object of the verb or preposition), “whom” is the appropriate choice. Ask yourself, “Whom is the action being done to?” This will help you determine if “whom” is correct.
For example: “Whom did you see at the party?” “Whom” is correct because the subject (you) is doing the action (seeing), and “whom” is the object (the person being seen).
The Subject vs Object Test: A Quick Way to Decide
How to Test if You Should Use Who or Whom
A simple trick to decide whether to use “who” or “whom” is to restructure the sentence and substitute the pronouns with “he/she” (for “who”) or “him/her” (for “whom”). If you would naturally use “he” or “she,” the correct choice is “who.” If you would use “him” or “her,” the correct choice is “whom.”
For example: “Who/Whom did you see?” Try replacing with “he” or “him”—”I saw him,” so “whom” is correct.
Examples of Applying the Test in Practice
For example: “Who/Whom is coming to dinner?” Replacing “who” with “he” gives “he is coming,” so “who” is correct.
Common Mistakes with Who vs Whom
Overusing Who When Whom Is Correct
One of the most common mistakes is overusing “who” in place of “whom.” This error happens because, in informal speech, “who” is often used for both subjects and objects. However, using “whom” correctly in formal writing and speech shows an understanding of the rules.
Misplacing Whom in a Sentence
Sometimes, “whom” is incorrectly placed in a sentence. It is easy to mix up the positions of “who” and “whom” because of their similar sounds, but their roles differ significantly in terms of grammatical structure.
Avoiding Common Grammatical Pitfalls
Many speakers and writers struggle with who vs whom, especially in complex sentences or after prepositions. One way to avoid mistakes is by consistently checking the role of the pronoun in the sentence and applying the subject-object test.
Practice Makes Perfect: Exercises to Master Who vs Whom
Fill-in-the-Blank Exercises to Practice the Correct Usage
Engaging in practice exercises can help reinforce the differences between “who” and “whom.” For instance, fill-in-the-blank sentences that test understanding in different contexts can help you solidify your knowledge of these pronouns.
How to Integrate Who vs Whom into Daily Conversation
By practicing these rules in daily conversation, you’ll become more comfortable distinguishing between “who” and “whom.” This consistent practice ensures that the right word is used automatically in both formal and informal contexts.
Conclusion: Becoming a Who vs Whom Pro
Mastering the difference between “who” and “whom” is a valuable skill in both formal and informal settings. With consistent practice and understanding of the rules, you’ll gain confidence in using these pronouns correctly. Keep practicing, and soon you’ll be a “who vs whom” expert in no time!
Sources
My name is Khamis Maiouf. I am the creator of the English Teacher Site, dedicated to providing valuable resources and insights for students around the world. With a passion for education and a commitment to helping students enhance their skills, I aim to make English teaching more effective and enjoyable for both educators and students.