Master English Tenses Fast: Give, Gave, Given Explained

Overview of “Give, Gave, Given” in English
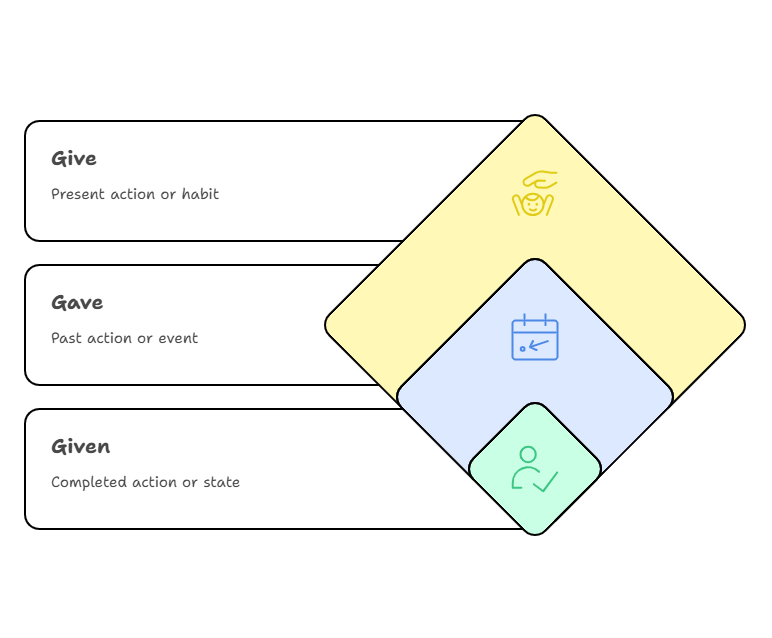
The verb “give” is a fundamental verb in English, used in different forms depending on the tense of the action.
- Give: Present tense; refers to something happening now or regularly.
- Gave: Past tense; refers to an action that occurred before.
- Given: Past participle; used with auxiliary verbs like “have” or “had” to connect past actions with the present or future.
Summary of Key Points:
- “Give” = Present
- “Gave” = Past
- “Given” = Past participle, used with auxiliary verbs
Understanding the Three Forms of “Give”
Goal: Dive deeper into the specific tenses and practical examples for each form.
Present Tense: “Give” Usage Explained
The present tense of “give” is used to describe actions that are happening now or regularly in the present or future.
- Example 1: I give gifts every year.
- Example 2: She gives me advice regularly.
Summary of Key Points:
- Simple present: Used for regular actions, facts, or habitual activities.
Past Tense: “Gave” Usage Explained
The past tense “gave” describes actions completed in the past.
- Example 1: I gave him a book last week.
- Example 2: She gave a speech yesterday.
Summary of Key Points:
- Simple past: Describes actions completed in the past.
Past Participle: “Given” Usage Explained
“Given” is the past participle of “give,” and is used with auxiliary verbs like “have” or “had” to connect past actions with the present or future.
- Example 1: I have given him the keys.
- Example 2: She had given her presentation before the meeting.
Summary of Key Points:
- Past participle: Used with auxiliary verbs to form perfect tenses.
Practical Examples of “Give, Gave, Given” in Different Tenses
Present Tense Examples
- Example 1: I give my time to the community every Saturday.
- Example 2: She gives lectures on environmental issues.
Past Tense Examples
- Example 1: I gave her a call earlier today.
- Example 2: They gave a wonderful performance last night.
Past Participle Examples
- Example 1: I have given all my belongings to charity.
- Example 2: He had given his explanation before they asked further questions.
Practice Exercises: Test Your Knowledge
Fill in the Blanks
- I __________ (give) her the pen yesterday.
- She __________ (give) me a present every year.
- They __________ (give) their best performance yet.
Answer Key:
- gave
- gives
- have given
Multiple Choice: Choose the Correct Option
- I __________ a great gift yesterday.
- a) give
- b) gave
- c) given
- She __________ a wonderful story at the party.
- a) gave
- b) gives
- c) given
- They __________ their time to the cause for years.
- a) gave
- b) have given
- c) give
Answer Key:
- b) gave
- a) gave
- b) have given
Common Learner Mistakes and Corrections
1. Mistake: Using “Give” in the Past Tense
Incorrect: I give her a gift yesterday.
Corrected: I gave her a gift yesterday.
2. Mistake: Using “Given” Instead of “Gave” for Past Actions
Incorrect: She given a speech at the event.
Corrected: She gave a speech at the event.
3. Mistake: Confusing Present and Past Participle Forms
Incorrect: I have gave him the book.
Corrected: I have given him the book.
Relevant Synonyms and Vocabulary
- Provide
- Hand
- Offer
- Bestow
- Deliver
- Donate
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: When should I use “give” vs. “gave”?
A1: Use “give” for actions happening in the present or future, and “gave” for actions completed in the past.
Q2: What’s the difference between “given” and “gave”?
A2: “Given” is the past participle, used with auxiliary verbs like “have” or “had,” while “gave” is the simple past tense.
Q3: Can I use “given” in a sentence without an auxiliary verb?
A3: No, “given” is usually paired with auxiliary verbs to indicate perfect tenses, such as “have” or “had.”
Sources
Dictionary, https://www.etymonline.com/word/advise.
Dictionary, https://www.etymonline.com/word/advice.
My name is Khamis Maiouf. I am the creator of the English Teacher Site, dedicated to providing valuable resources and insights for students around the world. With a passion for education and a commitment to helping students enhance their skills, I aim to make English teaching more effective and enjoyable for both educators and students.